Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sugaya, Toshikatsu; Nakatani, Takayoshi; Sakai, Akihiro
JAEA-Technology 2017-032, 21 Pages, 2018/01
[The article has been found to have a problem about reliability of the corrosion data acquisition, and thus it is unavailable to download the full text in accordance with authors' intentions to retract the report.] For the purpose of the setting of the rate of nuclide elution necessary to safety assessment, we planned the gas-accumulating type corrosion test on Zr-2.5wt%Nb alloy in order to obtain long-term corrosion rate under low temperature, low oxygen and alkaline conditions assuming the disposal environment. A corrosion rate over a testing period of 5 years is acquired with the aim to grasp a long-term corrosion rate behavior in this report. This corrosion rate is compared with the same data that was previously acquired over a testing period of 2 years. As a result, it is confirmed that an evaluation method that is proportional to the minus cubic root of corrosion time squared can be applicable to the corrosion rate behavior acquired this time over a testing period of 5 years, which is the same result in evaluating the corrosion rate behavior acquired over a testing period of 2 years.
Kitamura, Akira; Chikazawa, Takahiro*; Akahori, Kuniaki*; Tachi, Yukio
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 23(1), p.55 - 72, 2016/06
The Japanese geological disposal program has started researching disposal of spent nuclear fuel (SF) in deep geological strata (hereafter "direct disposal of SF") as an alternative management option other reprocessing followed by vitrification and geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste. We conducted literature survey of dissolution rate of SF matrix and constructing materials (e.g. zircaloy cladding and control rods) selected in safety assessment reports for direct disposal of SF in Europe and United States. We also investigated basis of release rate determination and assignment of uncertainties in the safety assessment reports. Furthermore, we summarized major conclusions proposed by some European projects governed by European Commission. It was found that determined release rates are fairly similar to each other due to use of similar literature data in all countries of interest. It was also found that the determined release rates were including conservativeness because it was difficult to assign uncertainties quantitatively. It is expected that these findings are useful as fundamental information for determination of the release rates for the safety assessment of Japanese SF disposal system.
Taniguchi, Naoki; Kawakami, Susumu; *
JNC TN8400 2001-025, 27 Pages, 2002/03
It is essential to understand the corrosion type of carbon steel under the repository conditions for the lifetime assessment of carbon steel overpack used for geological isolation of high-level radioactive waste. According to the previous study, carbon steel is hard to passivate in buffer material assuming a chemical condition range of groundwater in Japan. However, concrete support will be constructed around the overpack in the case of repository in the soft rock system and groundwater having a higher pH may infiltrate to buffer material. There is a possibility that the corrosion type of carbon steel will be influenced by the rise of the pH in groundwater. In this study, anodic polarization experiments were performed to understand the passivation condition of carbon steel in buffer material saturated with water contacted with concrete. An ordinary concrete and a low-alkalinity concrete were used in the experiment. The results of the experiments showed that the carbon steel can passivate under the condition that water having pH  13 infiltrate to the buffer material assuming present property of buffer material. If the low-alkalinity concrete is selected as the support material, passivation can not occur on carbon steel overpack. The effect of the factors of buffer material such as dry density and mixing ratio of sand on the passivation of carbon steel was also studied. The results of the study showed that the present property of buffer material is enough to prevent passivation of carbon steel.
13 infiltrate to the buffer material assuming present property of buffer material. If the low-alkalinity concrete is selected as the support material, passivation can not occur on carbon steel overpack. The effect of the factors of buffer material such as dry density and mixing ratio of sand on the passivation of carbon steel was also studied. The results of the study showed that the present property of buffer material is enough to prevent passivation of carbon steel.
Maki, Akira; ; Taguchi, Katsuya; ; Shimizu, Ryo; Shoji, Kenji;
JNC TN8410 2001-012, 185 Pages, 2001/04
"The third technological meeting of Tokai Reprocessing plant (TRP)" was held in JNFL Rokkasyo site on March 14 , 2001. The technical meetings have been held in the past two times. The first one was about the present status and future plan of the TRP and second one was about safety evaluation work on the TRP. At this time, the meeting focussed on the corrosion experrience, in-service inspection technology and future maintenance plan. The report contains the proceedings, transparancies and questionnaires of the meeting are contained.
, 2001. The technical meetings have been held in the past two times. The first one was about the present status and future plan of the TRP and second one was about safety evaluation work on the TRP. At this time, the meeting focussed on the corrosion experrience, in-service inspection technology and future maintenance plan. The report contains the proceedings, transparancies and questionnaires of the meeting are contained.
Taniguchi, Naoki; ; Kawasaki, Manabu*; Masugata, Tsuyoshi*
JNC TN8400 2001-001, 56 Pages, 2000/12
It is necessary to clear the effects of corrosion products on the corrosion life time of carbon steel overpack for geological isolation of high-level radioactive waste(HLW). Especially, it is important to understand the effects of magnetite because magnetite as a simulated corrosion product is reported to accelerate the corrosion rate of carbon steel. In this study, corrosion tests to reproduce the acceleration of corrosion due to magnetite was performed and the mechanism of the acceleration was investigated to evaluate the effects of magnetite as a corrosion product. Based on the results of experiments, following conclusions are obtained ; (1)Magnetite powder accelerates the corrosion rate of carbon steel. The main reaction of corrosion under the presence of magnetite is the reduction of Fe(III) in magnetite to Fe(II), but the reaction of hydrogen generation is also accelerated. The contribution of hydrogen generation reaction was estimated to be about 30% in the total corrosion reaction based on the experimental result of immersion test under the presence of magnetite. (2)Actual corrosion products containing magnetite generated by the corrosion of carbon steel protect the metal from the propagation of corrosion. The corrosion depth of carbon steel overpack due to magnetite was estimated to be about 1 mm based on the results of experiments. Even if the effect of magnetite is taken into the assessment of corrosion lifetime of overpack, total corrosion depth in 1000 years is estimated to be 33 mm, which is smaller than the corrosion allowance of 40 mm described in the second progress report on research and development for the geological disposal of HLM/ in Japan. It was concluded that the effect of magnetite on the corrosion life time of carbon steel overpack is negligible.
; Ohno, Shuji;
JNC TN2400 2000-006, 56 Pages, 2000/12
Sodium combustion analyses were performed using ASSCOPS version 2.1 in order to obtain background data for evaluating the validity of the mitigation system against secondary sodium leak of MONJU. The calculated results are summarized as follows. (1)Peak atmospheric pressure  4.3 kPa[gage] (2)Peak floor liner temperature
4.3 kPa[gage] (2)Peak floor liner temperature  870
870 C, Maximum thinning of liner
C, Maximum thinning of liner  2.6mm (3)Peak hydrogen concentration <2% (4)Peak floor liner temperature in the spilt sodium storage eell
2.6mm (3)Peak hydrogen concentration <2% (4)Peak floor liner temperature in the spilt sodium storage eell  400
400 C , Peak floor concrete temperature in the spilt sodium storage cell
C , Peak floor concrete temperature in the spilt sodium storage cell  140
140 C.
C.
Saburi, Tei; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Ueda, Satoshi*; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi
JAERI-Tech 2000-057, 23 Pages, 2000/10
no abstracts in English
Sumiyama, Morio*
JNC TJ8400 2000-009, 138 Pages, 2000/02
To evaluate corrosion behavior of carbon steel, a candidate materials of overpack, buried in soil for a long time, the water pipes buried in freshwater clay for a long time we digged out and the soil environment and the corrosion weight loss of pipes have been researched. From the results, a corrosion model (an empirical equation), an oxygen reduction reaction rate-determing step type, of carbon steel buried in soil was introduced. The corrosion data of under ground pipe collected by the Japan Community Gas Associations was used to increase reliability of the corrosion model equation. These data are one of researches of corrosion behavior of carbon steel buried in soil for a long time studied by at home and abroad. 38 samples buried freshwater clay were selected in 171 samples. With estimating the corrosion velocities and the soil environment factors of the above data, the maximum depth of pit corrosion was calculated by the statistical method of the extreme values using the area of overpack as the recurrent time. The correlation between the soil environment factors and the corrosion weight loss was obtained by the correlation analysis. The corrosion model of the maximum depth of pit corrosion at 0.99 of cumulative probability was compared between the under ground pipe data and the above data. On the reference data and the above data, the corrosion model equation; H = aY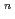 was compared with the maximum depth of pit corrosion at 0.99 cumulative probability. The data of water pipes and community gas pipes at 0.99 cumulative probability showed the reasonable values when these data were compared with the reference data. So that the model was proved as a good corrosion model m the neutral low dissolved oxygen environment.
was compared with the maximum depth of pit corrosion at 0.99 cumulative probability. The data of water pipes and community gas pipes at 0.99 cumulative probability showed the reasonable values when these data were compared with the reference data. So that the model was proved as a good corrosion model m the neutral low dissolved oxygen environment.
Honda, Takashi*; *
JNC TJ8400 2000-007, 200 Pages, 2000/02
In general, it is very difficult to evaluate the residual state of metallic iron and the original shape of iron-base archaeological artifacts, as these are covered by thick oxide films formed in the ground during over several hundred years. The purpose of this research is to quantify the corrosion of an artifact such as base, knife, and nail, which was digged out of the relics about 500-1,000 years old. (1)The outer oxide film layer and the inner metallic iron can be quantitatively divided by using X-ray CT method. Furthermore, the original surfaces of artifacts can be estimated from the obtained images, even if the metallic iron has corroded completely. The X-ray CT images were also compared with those obtained by X-ray transmission inspection. (2)The corrosion amounts and rates were evaluated on the basis of thicknesses, densities, and iron concentrations of oxide films. (3)The characteristic differences between ancient iron and modern carbon steel were evaluated by analyzing the ancient iron slag.
 O
O -NaOH System)
-NaOH System)Yoshida, Eiichi; Aoto, Kazumi; Hirakawa, Yasushi;
JNC TN9400 2000-024, 42 Pages, 1999/10
For the purpose of improving the reliability of evaluation, the corrosion rate equation of the carbon steel SM400B (JIS G3106) in the high-temperature sodium compounds (NaOH-Na 0
0 system) was revised. ln this revision, the data acquired after 1997 was used. Based on the experimental results, the evaluation was made to be an approach to the following; (1)Metal loss of carbon steel in NaOH-Na
system) was revised. ln this revision, the data acquired after 1997 was used. Based on the experimental results, the evaluation was made to be an approach to the following; (1)Metal loss of carbon steel in NaOH-Na 0
0 system was evaluated as increases in exposure to the time, which is linear rate law. (2)There were no significant effects of the experiment atmosphere and mixing speed of the reagent on corrosion rate. (3)The concentration of Na
system was evaluated as increases in exposure to the time, which is linear rate law. (2)There were no significant effects of the experiment atmosphere and mixing speed of the reagent on corrosion rate. (3)The concentration of Na 0
0 in sodium compound is considered for the evaluation. The concentration under experiment is made to be the over concentration necessary for maintaining the dominant reaction between Fe and Na
in sodium compound is considered for the evaluation. The concentration under experiment is made to be the over concentration necessary for maintaining the dominant reaction between Fe and Na 20
20 . As a result of the evaluation, the additional data are 67 points. The data for the revision of the evaluation equation became the total of 105 points, when existing data of 38 points were added. The statistical evaluation of 105 points was carried out, and following recommended equation was obtained. C
. As a result of the evaluation, the additional data are 67 points. The data for the revision of the evaluation equation became the total of 105 points, when existing data of 38 points were added. The statistical evaluation of 105 points was carried out, and following recommended equation was obtained. C = C exp(-Q/RT) Where; C
= C exp(-Q/RT) Where; C : Corrosion rate, mm/h C : Material constant Q : Apparent activation energy, cal/mol R : Gas constant, 1.986 cal/mol K T ; Absolute temperature, K Q = 9.61 kcal/mol C = 148.29 (average), 262.11 (99% UCL), 83.90 (99% LCL)
: Corrosion rate, mm/h C : Material constant Q : Apparent activation energy, cal/mol R : Gas constant, 1.986 cal/mol K T ; Absolute temperature, K Q = 9.61 kcal/mol C = 148.29 (average), 262.11 (99% UCL), 83.90 (99% LCL)
Ioka, Ikuo; Onuki, Kaoru; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Kuriki, Yoshiro*; Nagoshi, Masayasu*; Nakajima, Hayato; Shimizu, Saburo
Ryusan To Kogyo, 52(4), p.1 - 6, 1999/04
no abstracts in English
*; Nishimura, Tsutomu*; Shimogori, Kazutoshi*; *; Fujiwara, Kazuo*; *; *
PNC TJ1058 97-005, 49 Pages, 1997/03
None
*; Nishimura, Tsutomu*; Shimogori, Kazutoshi*; *; Fujiwara, Kazuo*; *; *
PNC TJ1058 97-004, 179 Pages, 1997/03
None
Wada, Ryutaro*; Nishimura, Tsutomu*; Fujiwara, Kazuo*; *; *
PNC TJ1058 97-003, 33 Pages, 1997/03
None
Wada, Ryutaro*; Nishimura, Tsutomu*; Fujiwara, Kazuo*; *; *
PNC TJ1058 97-002, 430 Pages, 1997/03
None